Customize
Change configuration#
There are a lot of configuration options available and documented in the Configuration section. The keys in the configuration documentation are always in the form of:
client/html/catalog/filter/default/button = 1
As a rule of thumb, replace the slashes (/) with dots (.) to use such keys in TypoScript:
client.html.catalog.filter.button = 1
Warning
Don't forget the prefixes necessary for frontend (plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.) and backend (module.tx_aimeos.settings.) settings! Also, the dot-notation only applies to the key on the left-hand side of the equal sign, not to the value on the right-hand side, i.e.
client.html.catalog.lists.template-body = catalog/lists/body-mytemplate
Frontend#
To add or overwrite configuration options in TYPO3, you can use TypoScript. Simply add the new or overwritten configuration values to the setup section of a page TypoScript template, e.g.:
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.client.html.catalog.filter.button = 1
If the configuration key accepts an array of values, add them like this:
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.client.html.catalog.filter.subparts {
0 = search
1 = tree
2 = attribute
}
In case you want to limit related items by their list type or fetch additional items for suppliers or categories, then use:
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.client.html.catalog.lists.domains {
text = text
product {
0 = default
}
supplier {
0 = text
1 = media
}
catalog {
0 = text
1 = media
}
}
Per Plugin#
Several plugins provide the possibility to add plug-in specific TypoScript configuration in the "Plugin" tab of the plug-ins placed on a page. Use the configuration keys from the documentation as in the example below:
client.html.catalog.filter.button = 1
Each slash (/) is replaced by a dot (.), nothing is prepended. The same is true for arrays of values as well. Please have a look at the frontend section above for an example.
PageTS#
In order to configure a plugin's behaviour in the backend, TYPO3 uses what is called a "page typoscript" (pageTS). Aimeos offers only one such configuration option, the "site selection", which is only needed, when you run a multiple shop setup:
tx_aimeos.mshop.locale.site = myshop
This setting will change e.g. which categories are displayed in the plugin options view of the catalog filter plugin. In order to change this setting, you have to edit the page and go to the "Resources" tab. There is a text area where you can add the line above.
Admin backend#
Like the frontend, the Aimeos administration interface in TYPO3's backend can be configured as well. It is implemented as a TYPO3 backend module which means that the the respective TypoScript configurations must be prefixed with "module.tx_aimeos.settings.", e.g.:
module.tx_aimeos.settings.mshop.locale.site = myshop
It doesn't make sense to assign all frontend settings to the backend module, too. This would only slow down loading the administration interface. There are only a few settings you may want to share between frontend and backend for the same page, namely the "mshop.locale.site" setting.
Scheduler#
All scheduler tasks allow adding specific TypoScript configuration for the jobs that should be executed. This is especially useful for setting or overwriting configuration values for e-mails that should be sent to customers. Use the configuration keys from the documentation like this:
client.html.email.payment.template-body = email/payment/body-standard
The same works with arrays of values as well:
client.html {
email.payment.template-body = email/payment/body-standard
}
controller.jobs.order.email.payment.status {
0 = 5
1 = 6
}
Overwrite translations#
There is the possibility to overwrite translations from the core or other Aimeos extensions via TypoScript. This is very comfortable if you only want to replace certain existing translations with your own ones. For each translation, you need the ISO language code, the translation domain, the original string and the new translation, e.g.:
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.i18n.<ISO language code>.<number> {
domain = <translation domain>
string = <original English singular from source code>
trans = <new translation>
}
Warning
This should only be used to replace a few translations! If you would like to translate Aimeos to a new language, please use the Transifex website instead. It will be available in the next Aimeos release automatically. Also, if you need to overwrite more than a few translations, you should read the article about adding translations.
Required information#
- ISO language code
- To specify the language for the translation, a two letter ISO language code (639-1) is necessary (e.g. "en"). It is also possible to add the two letter ISO country code to refer to country-specific language variants like "en_GB" for British English. You can use all languages that are mapped via TypoScript from the TYPO3 language IDs. Please make sure the language code is always in lower case while the the optional country code is always in upper case.
- number
- This is a continuous number to distinguish between the different translations added to the TypoScript configuration. If you are using a number twice, the latter translation definition will overwrite the former one.
- domain
- The "translation domain" where the original string stems from. The Aimeos core has six translation domains: "mshop" (core lib with managers), "controller/frontend" (basic business logic for the frontend), "client" (frontend HTML parts), "controller/jobs" (asynchronous cronjob tasks) and "admin" (administration interface). To figure out the domain where a string originates from, look at the ".pot" files in the Aimeos core.
- string
- The original singular string from the source code or the .pot file. The string must be exactly the same (character case, white spaces, etc.) as in the English source code / .pot file! You can not use an already translated string as source.
- trans
- The new translation for the original string. This can be also an array, if one or more plural forms are necessary.
Warning
The original string is case sensitive so it makes a difference if you use "Basket" or "basket"! Always use the same string as used in the template or source code.
Singular translations#
A simple singular translation to English:
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.i18n.en.0 {
domain = client
string = address
trans = Address
}
A simple singular translation to US English:
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.i18n.en_US.0 {
domain = client
string = Basket
trans = Cart
}
Several singular translations to English:
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.i18n.en {
0 {
domain = client
string = Basket
trans = Cart
}
1 {
domain = client
string = address
trans = Address
}
}
Plural translation to English:
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.i18n.en.0 {
domain = client
string = address
trans {
0 = Address
1 = Addresses
}
}
Plural translations#
A translation including one or more plural forms can be defined if the original string in the source code also supports plurals. Two methods are available to perform proper translation of plural strings: translate() and dn().
$this->translate( '<domain>', '<singular>, '<plural>', <count> )
$i18n->dn( '<domain>', '<singular>, '<plural>', <count> )
To overwrite a plural translation, the simplest form is:
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.i18n.<ISO language code>.<number> {
domain = <translation domain>
string = <original singular>
trans {
0 = <singular translation>
<index> = <plural translation>
}
The index "0" is always the singular translation. Most languages only have one plural form, so it must be defined by using the index "1". But some languages use several plural forms depending on the count given in the last parameter of the translation method. In this case, the index depends on the language and the value of count. To find out the right index for the language, you have to have a look into the getPluralIndex() method that maps count to the index of the proper plural form of the language you want to translate to. An example for Czech would be:
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.i18n.cz.0 {
domain = client
string = hour
trans {
# one hour
0 = dlouhá hodina
# two to four hours
1 = dlouhé hodiny
# more than four hours
2 = dlouhých hodin
}
}
Special characters#
Sometimes, the source string, that should be translated, contains special characters like new lines (\n) or backslashes (). This is no problem if you place them in a ".po" file of your project specific extension (same location as the original ".po" file) and transform its content using the Unix Gettext command, e.g.:
msgfmt -c -o de de.po
Using them in TypoScript is more difficult because TypoScript doesn't allow new lines in values. Therefore, you have to use "\n" (a backslash and the character "n") as replacement:
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.i18n.de.0 {
domain = client
string = The payment was canceled.\nDo you wish to retry your order?
trans = Die Zahlung wurde abgebrochen.\nMöchten Sie Ihre Bestellung wiederholen?
If the source translation contains a backslash, it must be preserved in TypoScript:
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.i18n.de.0 {
domain = client
string = You\'ve chosen to pay in advance
trans = Sie haben Vorauskasse gewählt
Fluid templates#
All Aimeos templates are written in PHP using a template engine and view helpers that are easy to understand. It works in all integrations in the same way, is extremely fast and doesn't require you as developer to learn a new syntax.
Alternatively, you can use the TYPO3 Fluid template engine for Aimeos templates overwritten for your project. Thus, all your templates will be in the same template language.
Tip
The Aimeos templates contain nested objects and their methods sometimes needs arguments. To be able to call these methods within Fluid templates, you need to install the VHS view helper extension and use the v:call() view helper.
To replace an Aimeos PHP template by our own Fluid template, the Fluid template needs to be stored at the same location as the Aimeos PHP template, i.e. at the ./client/html/templates/ folder of your project-specific Aimeos extension. It is also required to preserve the underlying directory structure as well as to abide by the file naming convention (<template-name>.html), e.g.:
./client/html/templates/catalog/detail/body-standard.html
The file extension .html is important in order to be recognized as template that should be processed by the Fluid engine.
The Fluid view helpers available by default can't give you access to all data you need. Therefore, the Aimeos package contains some view helpers to retrieve data from Aimeos specific sources like configuration settings or translations. You have to include these view helpers by adding the appropriate namespace to the Fluid template before using them:
{namespace ai=Aimeos\Aimeos\ViewHelper}
Configurations#
{ai:config(key: 'key/to/config', default: '' )}
<ai:config key="key/to/config" default="" />
The ai:config view helper retrieves the Aimeos settings for a given key, e.g. client/html/catalog/lists/basket-add. If no value is found for the key, the given default value (optional) is returned instead.
Translations#
{ai:translate(singular: 'string for singular', plural: 'string for plural', number: 1, arguments: {0: 10, 1: 'value'}, domain: 'client', escape: true)}
<ai:translate singular="string for singular" plural="string for plural" number="1" arguments="{0: 10, 1: 'value'}" domain="client" escape="true" />
The ai:translate view helper retrieves the translated value from the Aimeos "Gettext" files. It is similar to the f:translate view helper and useful for translating singular and plural phrases, e.g.:
{ai:translate(singular: '%1$d apple', plural: '%1$d apples', number: 10, arguments: {0: 10})}
When the third parameter is "1", the function returns "1 apple", and for values greater than 1 it returns e.g. "10 apples". The method takes care of the various plural rules for all languages.
If the fourth argument (arguments) contains values, they will be used to replace the placeholders in the translated string. Internally, the vsprintf() method takes care of that.
The domain argument is the same one that is used in the Aimeos $this->translate() view helper. In the frontend it is either "client" or "client/code" while for templates in the administration interface it is "admin".
If you don't want the output to be escaped (i.e. HTML tags returned as source), set the escape argument to false.
Note
All arguments besides "singular" are optional.
Blocks#
The Aimeos template engine has a "block" view helper to save a rendered template, so it can be inserted into another template. This is very similar to the f:section tag of the Fluid template engine. It is therefore recommended to replace an Aimeos block view helper statement...
<?php $this->block()->start( 'cataog/detail/actions' ); ?>
<div class="actions">
...
</div>
<?php $this->block()->stop(); ?>
<?php echo $this->block()->get( 'catalog/detail/actions' ); ?>
... with a Fluid section tag:
<f:section name="catalog/detail/actions">
<div class="actions">
...
</div>
</f:section>
<f:render section="catalog/detail/actions" arguments="{...}"/>
Multiple shops#
In Aimeos terms, a "shop" is a "site". Therefore, when discussing whether the system can handle "mutlipe shops", we say that Aimeos is multi-site capable. It allows to store several shops in one database.
Follow these steps to create and manage multiple Aimeos sites:
-
Create a new TYPO3 page#
Each shop needs its individual TYPO3 page tree section. Therefore, create a new page that is located outside of any other potential Aimeos site that might already exist.
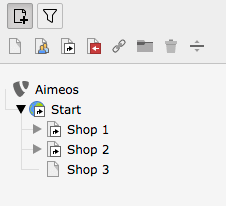
It is even possible to import the .t3d package that Aimeos provides into the new page.
-
Create the new site in the Extension Manager#
In the Extension Manager, go to the Aimeos configuration settings. Enter a new "site code" for which a new site will be created. (If it already exists, it will be updated with the required entries for the used extension version, in case you have updated to a newer Aimeos version.)
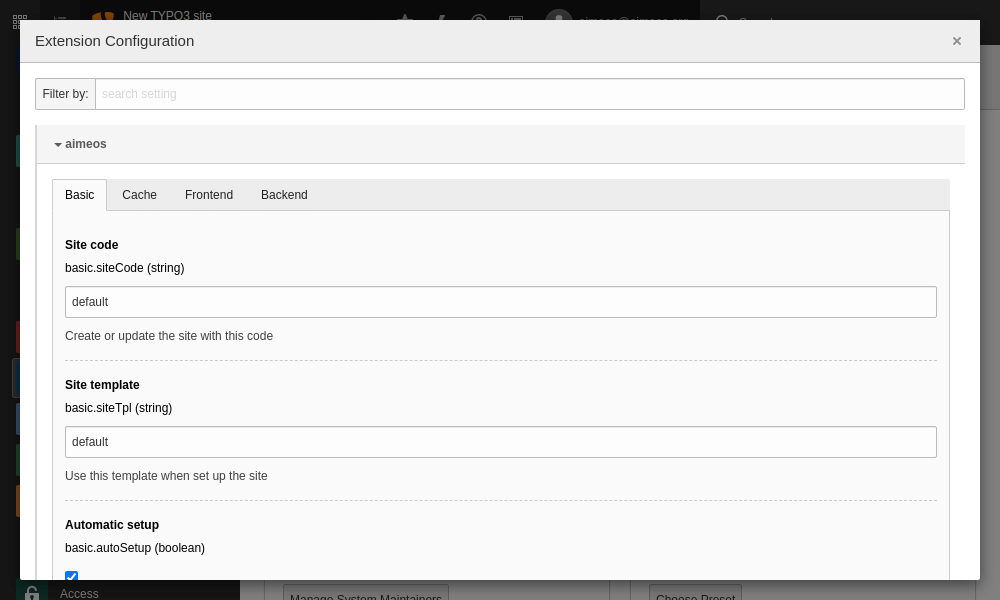
- Admin Tools::Settings:
- Search for "aimeos"
- Enter a new site code in the corresponding input field
- Save and return
- Admin Tools::Extensions:
- Click on the update icon of the Aimeos extension
The "update" function runs through a list of checks. Once this check has finished executing, you'll be presented with the types of data that have been added to the new site.
Warning
If you update Aimeos from a previous version, you need to run the update script for all sites you've created! Otherwise, required records may be missing and existing data isn't migrated.
- Admin Tools::Settings:
-
Create the new "Aimeos locale"#
In the Aimeos administraion interface of the TYPO3 backend, open the "Locales" menu and click on "Sites":
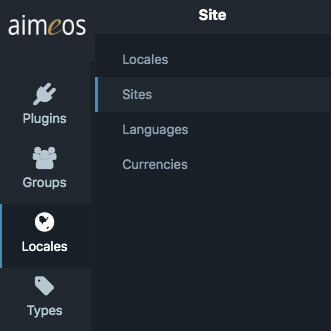
Add a new site:
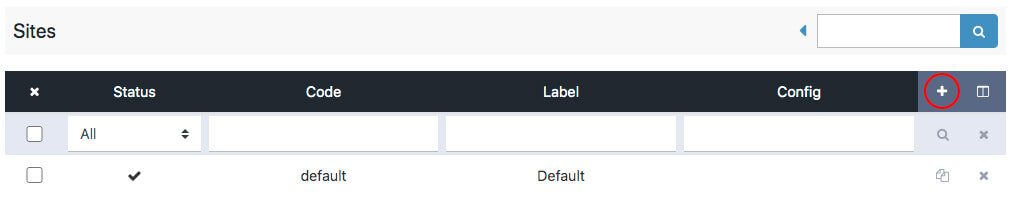
Enter the new "site code" in the required "Code" field:
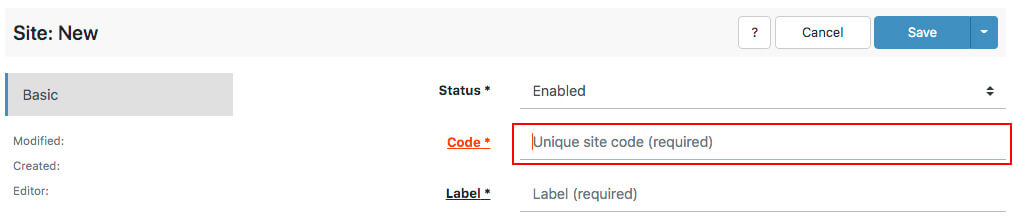
Finally click "Save" in the upper right corner.
-
Add pageTS config#
Back in TYPO3's page tree, go to the root page of the newly created shop/site. In order to display the appropriate data of the respective (second, third,...) shop/site, add an additional setting to the page's pageTS field:
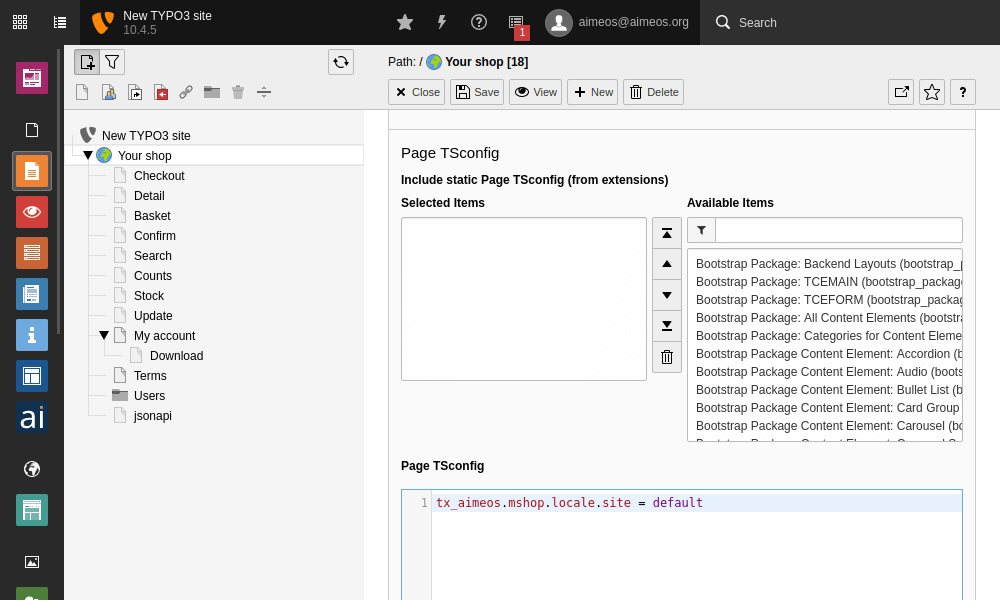
- Web::Page
- Select the root site of the new page tree
- Edit page
- Tab Resources, section TypoScript Configuration
tx_aimeos.mshop.locale.site = <code of site>Click on the icon for Save and close document at the top to store the change. Repeat these steps for each page tree where an different shop site other than the "default" site should be used. Clear all TYPO3 caches when you are done.
- Web::Page
-
TypoScript config#
To tell the frontend which shop/site to use in the new site's page tree, add a line of TypoScript to the setup configuration:
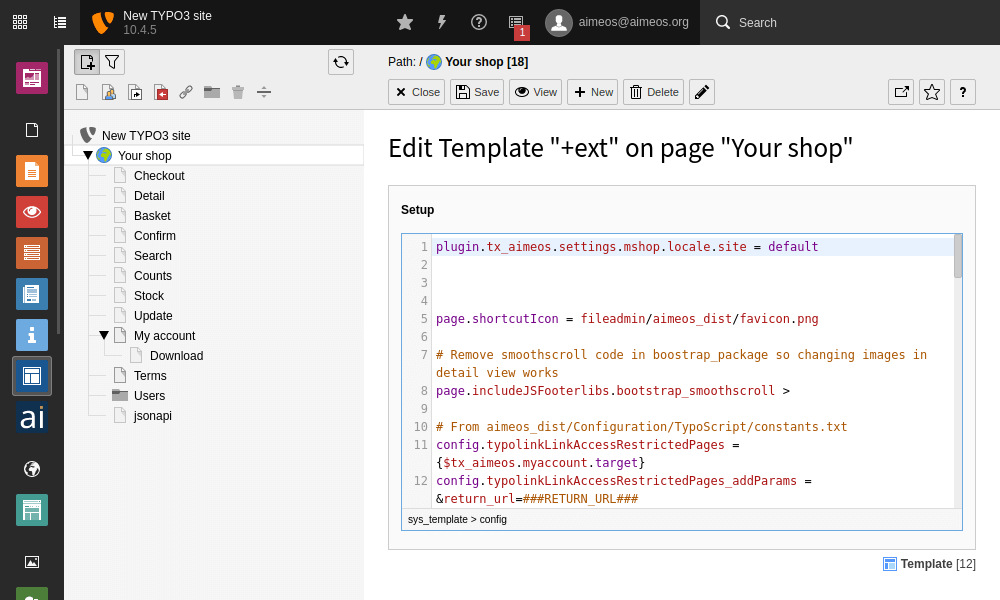
- Web::Template
- Select the new site's page tree root
- Choose Info/Modify in the drop-down at the top
- Click on Setup in the box below
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.mshop.locale.site = <code of site>Click on the icon for Save and close document at the top to store the change. Repeat these steps for each page tree where another shop site other than the "default" site should be used. Clear all TYPO3 caches when you are done.
- Web::Template
-
Site parameter#
Users can switch between multiple shops if the
loc-siteparameter is included in the URL. You can configure the name of the parameter (loc-siteby default) to a different name in the TypoScript setup section:plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.typo3.param.name.site = <name of the site parameter>For example, if you use the parameter "C" for the countries and that matches the site code, too, then you have to add this configuration to your TypoScript setup:
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.typo3.param.name.site = C -
Update multiple shops#
If you decide to upgrade to a newer version of Aimeos, it is required to run the Aimeos update script in the Extension Manager for each and every shop/site separately.
In order to get the code of a specific shop/site, go to "Aimeos Locales", choose "Sites" from its submenu and then one of the shops. You will find the site's unique code in the required field "Code". (Please have a look at step 3 for details on how to get to the Aimeos Locales and its site settings.)
Next, enter the code in the Aimeos extension settings and run the update script. (Please have a look at step 2 for a detailed description on how to get to the Aimeos extension settings.)
Repeat these steps for every shop you administer.
-
Disable, archive, review or delete a site#
Since these actions are independet of the host application (in this case TYPO3), please refer to the appropriate section in the manual to learn more about how to handle these scenarios.
Just keep in mind to check any TypoScript settings that might need re-configuration and to clear all TYPO3 caches once you are done, as well as to reload the TYPO3 backend. You might also want to take appropriate care of the respective TYPO3 page of the Aimeos site in question, e.g. disabling it, in order to prevent erroneous page renderings in the front end.
-
More info in the user manual#
It is recommended to also read up on the user manual's section that is dedicated to the use of multiple sites: Working with sites
Basket in navigation#
Most e-commerce sites show a small basket at the top right corner of each page. The Aimeos TYPO3 extension provides a plug-in for a small basket, too, containing only the number of products and the total value. You can either add this basket plug-in by
- placing the plug-in inside a column of a backend page layout
- assigning the plug-in output to a TypoScript object used in your Fluid layout
Tip
Using a Typoscript object for the basket doesn't require a column in the backend page layout which tends to be easier understandable by editors as long as they shouldn't be able to place the basket plug-in themselves.
TypoScript object#
The following TypoScript code must be placed in a TypoScript setup template. One such place could be a *.typoscript file in your ./fileadmin/ directory that is included in the setup section of your site. For example, create a ./fileadmin/setup.typoscript file with the following content:
lib.navigation.basket = COA
lib.navigation.basket.10 = USER
lib.navigation.basket.10 {
# userFunc = tx_extbase_core_bootstrap->run
userFunc = TYPO3\CMS\Extbase\Core\Bootstrap->run
vendorName = Aimeos
extensionName = Aimeos
pluginName = basket-small
controller = Basket
action = small
settings =< plugin.tx_aimeos.settings
}
Afterwards, you have to add an include statement in the Web::Template -> Setup section of your root page:
<INCLUDE_TYPOSCRIPT: source="FILE:fileadmin/setup.typosript">
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.client.html.basket.standard.url.target = <page ID of your basket page>
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.client.jsonapi.url.target = <page ID of your JSON API page>
You can find more about TypoScript includes in the documentation of TYPO3. Don't forget to replace the placeholders with the proper page ID of your basket page (without the angle brackets!). Otherwise, the small basket won't link to your basket page.
Afterwards, the output of the plug-in is available as cObject in your Fluid templates:
<f:cObject typoscriptObjectPath="lib.navigation.basket" />
Show in navigation#
The TYPO3 bootstrap_package makes it very easy to create a site using of a responsive web layout. To add the small basket to the navigation bar, you have to modify the navigation partial. Instead of changing the file in the bootstrap_package directly, you should create your own extension and add your version of this file there:
- Create a new extension using the extension builder
- Copy the
./Resources/Private/Partials/Page/directory to your extension using the same directory structure - Adapt the navigation partial in
./Resources/Private/Partials/Page/Navigation/Main.html - Add the Fluid condition as the first child element inside the
<div class="container">element:
<div class="container">
<f:if condition="{f:cObject(typoscriptObjectPath:'lib.navigation.basket')}">
<f:cObject typoscriptObjectPath="lib.navigation.basket" />
</f:if>
...
</div>
Afterwards, add this TypoScript configuration to Web::Template -> Constants telling the bootstrap_package to look for the partials inside your extension:
page.fluidtemplate.partialRootPath = EXT:<your extension name>/Resources/Private/Partials/Page/
Now the small basket should be displayed in the navigation bar on top of your site and you can start styling the HTML.
Tip
Don't forget to activate your extension in the extension manager!
Countries, states and regions#
Countries#
If you want to ship your products to several countries or you need to know from which countries your customers are, you have to enable the country selection in the address page of the checkout process.
By default, the country list is hidden for the billing and delivery address in the checkout process. To display them as mandatory fields you need to add "order.base.address.countryid" to the list of values defined in
In TYPO3 this is configured for billing and delivery addresses via TypoScript:
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.client.html.checkout.standard.address {
billing.mandatory {
0 = order.base.address.salutation
1 = order.base.address.firstname
2 = order.base.address.lastname
3 = order.base.address.address1
4 = order.base.address.postal
5 = order.base.address.city
6 = order.base.address.languageid
7 = order.base.address.email
8 = order.base.address.countryid
}
delivery.mandatory < .billing.mandatory
}
If no selection should be enforced, use these settings instead:
To define the country for billing and delivery addresses as optional, use this TypoScript configuration:
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.client.html.checkout.standard.address {
billing.optional {
0 = order.base.address.salutation
1 = order.base.address.firstname
2 = order.base.address.lastname
3 = order.base.address.address1
4 = order.base.address.postal
5 = order.base.address.city
6 = order.base.address.languageid
7 = order.base.address.email
8 = order.base.address.countryid
}
delivery.optional < .billing.optional
}
The list of countries is defined by the values added to the configuration key client/html/checkout/address/countries. The TypoScript below will add all countries worldwide to the select boxes for the billing and delivery address:
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.client.html.checkout.standard.address.countries {
0 = AD
# Andorra
1 = AE
# United Arab Emirates
2 = AF
# Afghanistan
3 = AG
# Antigua and Barbuda
4 = AI
# Anguilla
5 = AL
# Albania
6 = AM
# Armenia
7 = AO
# Angola
8 = AQ
# Antarctica
9 = AR
# Argentina
10 = AS
# American Samoa
11 = AT
# Austria
12 = AU
# Australia
13 = AW
# Aruba
14 = AX
# Åland Islands
15 = AZ
# Azerbaijan
16 = BA
# Bosnia and Herzegovina
17 = BB
# Barbados
18 = BD
# Bangladesh
19 = BE
# Belgium
20 = BF
# Burkina Faso
21 = BG
# Bulgaria
22 = BH
# Bahrain
23 = BI
# Burundi
24 = BJ
# Benin
25 = BL
# Saint Barthélemy
26 = BM
# Bermuda
27 = BN
# Brunei Darussalam
28 = BO
# Bolivia, Plurinational State of
29 = BQ
# Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba
30 = BR
# Brazil
31 = BS
# Bahamas
32 = BT
# Bhutan
33 = BV
# Bouvet Island
34 = BW
# Botswana
35 = BY
# Belarus
36 = BZ
# Belize
37 = CA
# Canada
38 = CC
# Cocos (Keeling) Islands
39 = CD
# Congo, the Democratic Republic of the
40 = CF
# Central African Republic
41 = CG
# Congo
42 = CH
# Switzerland
43 = CI
# Côte d'Ivoire
44 = CK
# Cook Islands
45 = CL
# Chile
46 = CM
# Cameroon
47 = CN
# China
48 = CO
# Colombia
49 = CR
# Costa Rica
50 = CU
# Cuba
51 = CV
# Cape Verde
52 = CW
# Curaçao
53 = CX
# Christmas Island
54 = CY
# Cyprus
55 = CZ
# Czech Republic
56 = DE
# Germany
57 = DJ
# Djibouti
58 = DK
# Denmark
59 = DM
# Dominica
60 = DO
# Dominican Republic
61 = DZ
# Algeria
62 = EC
# Ecuador
63 = EE
# Estonia
64 = EG
# Egypt
65 = EH
# Western Sahara
66 = ER
# Eritrea
67 = ES
# Spain
68 = ET
# Ethiopia
69 = FI
# Finland
70 = FJ
# Fiji
71 = FK
# Falkland Islands (Malvinas)
72 = FM
# Micronesia, Federated States of
73 = FO
# Faroe Islands
74 = FR
# France
75 = GA
# Gabon
76 = GB
# United Kingdom
77 = GD
# Grenada
78 = GE
# Georgia
79 = GF
# French Guiana
80 = GG
# Guernsey
81 = GH
# Ghana
82 = GI
# Gibraltar
83 = GL
# Greenland
84 = GM
# Gambia
85 = GN
# Guinea
86 = GP
# Guadeloupe
87 = GQ
# Equatorial Guinea
88 = GR
# Greece
89 = GS
# South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
90 = GT
# Guatemala
91 = GU
# Guam
92 = GW
# Guinea-Bissau
93 = GY
# Guyana
94 = HK
# Hong Kong
95 = HM
# Heard Island and McDonald Islands
96 = HN
# Honduras
97 = HR
# Croatia
98 = HT
# Haiti
99 = HU
# Hungary
100 = ID
# Indonesia
101 = IE
# Ireland
102 = IL
# Israel
103 = IM
# Isle of Man
104 = IN
# India
105 = IO
# British Indian Ocean Territory
106 = IQ
# Iraq
107 = IR
# Iran, Islamic Republic of
108 = IS
# Iceland
109 = IT
# Italy
110 = JE
# Jersey
111 = JM
# Jamaica
112 = JO
# Jordan
113 = JP
# Japan
114 = KE
# Kenya
115 = KG
# Kyrgyzstan
116 = KH
# Cambodia
117 = KI
# Kiribati
118 = KM
# Comoros
119 = KN
# Saint Kitts and Nevis
120 = KP
# Korea, Democratic People's Republic of
121 = KR
# Korea, Republic of
122 = KW
# Kuwait
123 = KY
# Cayman Islands
124 = KZ
# Kazakhstan
125 = LA
# Lao People's Democratic Republic
126 = LB
# Lebanon
127 = LC
# Saint Lucia
128 = LI
# Liechtenstein
129 = LK
# Sri Lanka
130 = LR
# Liberia
131 = LS
# Lesotho
132 = LT
# Lithuania
133 = LU
# Luxembourg
134 = LV
# Latvia
135 = LY
# Libya
136 = MA
# Morocco
137 = MC
# Monaco
138 = MD
# Moldova, Republic of
139 = ME
# Montenegro
140 = MF
# Saint Martin (French part)
141 = MG
# Madagascar
142 = MH
# Marshall Islands
143 = MK
# Macedonia
144 = ML
# Mali
145 = MM
# Myanmar
146 = MN
# Mongolia
147 = MO
# Macao
148 = MP
# Northern Mariana Islands
149 = MQ
# Martinique
150 = MR
# Mauritania
151 = MS
# Montserrat
152 = MT
# Malta
153 = MU
# Mauritius
154 = MV
# Maldives
155 = MW
# Malawi
156 = MX
# Mexico
157 = MY
# Malaysia
158 = MZ
# Mozambique
159 = NA
# Namibia
160 = NC
# New Caledonia
161 = NE
# Niger
162 = NF
# Norfolk Island
163 = NG
# Nigeria
164 = NI
# Nicaragua
165 = NL
# Netherlands
166 = NO
# Norway
167 = NP
# Nepal
168 = NR
# Nauru
169 = NU
# Niue
170 = NZ
# New Zealand
171 = OM
# Oman
172 = PA
# Panama
173 = PE
# Peru
174 = PF
# French Polynesia
175 = PG
# Papua New Guinea
176 = PH
# Philippines
177 = PK
# Pakistan
178 = PL
# Poland
179 = PM
# Saint Pierre and Miquelon
180 = PN
# Pitcairn
181 = PR
# Puerto Rico
182 = PS
# Palestine, State of
183 = PT
# Portugal
184 = PW
# Palau
185 = PY
# Paraguay
186 = QA
# Qatar
187 = RE
# Réunion
188 = RO
# Romania
189 = RS
# Serbia
190 = RU
# Russian Federation
191 = RW
# Rwanda
192 = SA
# Saudi Arabia
193 = SB
# Solomon Islands
194 = SC
# Seychelles
195 = SD
# Sudan
196 = SE
# Sweden
197 = SG
# Singapore
198 = SH
# Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
199 = SI
# Slovenia
200 = SJ
# Svalbard and Jan Mayen
201 = SK
# Slovakia
202 = SL
# Sierra Leone
203 = SM
# San Marino
204 = SN
# Senegal
205 = SO
# Somalia
206 = SR
# Suriname
207 = SS
# South Sudan
208 = ST
# Sao Tome and Principe
209 = SV
# El Salvador
210 = SX
# Sint Maarten (Dutch part)
211 = SY
# Syrian Arab Republic
212 = SZ
# Swaziland
213 = TC
# Turks and Caicos Islands
214 = TD
# Chad
215 = TF
# French Southern Territories
216 = TG
# Togo
217 = TH
# Thailand
218 = TJ
# Tajikistan
219 = TK
# Tokelau
220 = TL
# Timor-Leste
221 = TM
# Turkmenistan
222 = TN
# Tunisia
223 = TO
# Tonga
224 = TR
# Turkey
225 = TT
# Trinidad and Tobago
226 = TV
# Tuvalu
227 = TW
# Taiwan
228 = TZ
# Tanzania, United Republic of
229 = UA
# Ukraine
230 = UG
# Uganda
231 = UM
# United States Minor Outlying Islands
232 = US
# United States
233 = UY
# Uruguay
234 = UZ
# Uzbekistan
235 = VA
# Vatican City State (Holy See)
236 = VC
# Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
237 = VE
# Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of
238 = VG
# Virgin Islands, British
239 = VI
# Virgin Islands, U.S.
240 = VN
# Viet Nam
241 = VU
# Vanuatu
242 = WF
# Wallis and Futuna
243 = WS
# Samoa
244 = YE
# Yemen
245 = YT
# Mayotte
246 = ZA
# South Africa
247 = ZM
# Zambia
248 = ZW
# Zimbabwe
}
States and regions#
For each country you can freely define a list of states or regions that can be used afterwards to calculate the final price for each delivery option. To define states or regions via TypoScript use something like this:
plugin.tx_aimeos.settings.client.html.checkout.standard.address.states {
US {
CA = California
NY = New York
...
}
EU {
W = Western Europe
C = Central Europe
...
}
}
The key you have chosen for the state or region will be stored in the order address of the customer and can then be used during the rest of the checkout process. More details can be found in client/html/checkout/address/states.